2004-9
Thermophysical Property Measurements of Non-equilibrium Melts using an Electromagnetic Levitator in a Static Magnetic Field
静磁場を重畳した電磁浮遊法による非平衡メルトの熱物性測定
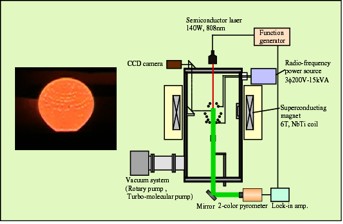
The purpose of the present study is to develop a novel technique for measuring thermophysical properties of chemically reactive, high-temperature, metallic or semiconductor melts using an electromagnetic levitator incorporating a static magnetic field. Not only oscillation of center of gravity of molten silicon droplet but also its surface oscillation diminished with increasing magnetic field. The silicon droplet rotated like the rigid body. The figure shows a recalescence of the silicon droplet under a static magnetic field of 3 T. In the next step, a modulation calorimetry using a laser heating is attempted to a silicon droplet in a static magnetic field to measure heat capacity, total hemispherical emissivity and thermal conductivity of molten silicon.
IMRAM, Tohoku University: H. Fukuyama, H. Kobatake, I. Minato
IMR, Tohoku University: S. Awaji
静磁場と電磁浮遊技術を組み合わせ,高温で化学活性な金属・半導体メルトの高精度熱物性測定装置(右図)を開発することを目的とする.電磁力により浮遊したシリコン液滴に静磁場を印加すると,ローレンツ力により,液滴の重心振動および表面振動が共に抑制されあたかも地球の自転のように剛体球運動する様子が観察された.3Tの静磁場中で初めてシリコン液滴のリカレッセンスを観察した(左図).凝固が開始すると液滴が軸を中心に回転している様子も観察された.今後,液滴上部からレーザー交流加熱により,熱容量,半球全放射率,熱伝導率の測定を行う.
東北大学多元物質科学研究所:福山博之,小畠秀和,湊 出
東北大学金属材料研究所:淡路 智
